Energy Transition
Domain Expertise
Expertise to accelerate the Energy Transition across the value chain
The Energy Transition is a profound, complex transformation impacting every aspect of modern life, with vital consequences for the world as we know it. It is embraced by all through a myriad of initiatives, some disjointed, some with conflicting outcomes. The ambitions are massive but the road remains bumpy and uncertain. Overwhelming. So, where to start …
Let us try with an analogy drawn from Le Petit Prince, the modern classic by Antoine de Saint Exupéry.
The tale features a pilot stranded in the desert with limited food supplies (our modern world), very focused on trying to fix his plane (our own daily preoccupations, all vital for sure), when a peculiar young person, le Petit Prince, emerges unexpectedly (Greta Thunberg, you, us) and engages with the aviator with an open-mind and curiosity allowing to see and rebuild our world around true essentials (the opportunities enabling the Energy Transition, and more broadly ESG sustainability). The pilot and le Petit Prince befriend by drawing simple forms, each subject to various interpretations, yet the two surprisingly align on what they see.
You can see below our attempt at drawing the Energy Transition …
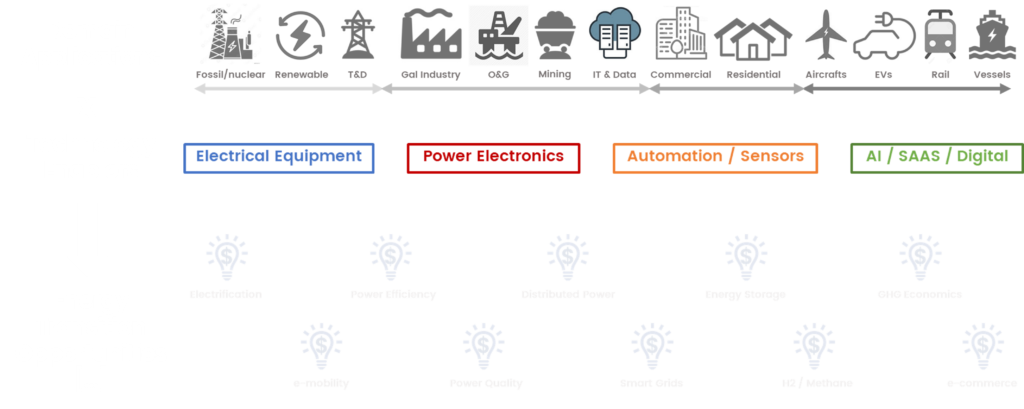
That may not yet resonate … let us try harder.
The Energy Transition applies in many different shapes and forms across the economy. Each industry segment, each stakeholder across the value chain, is set to define their own paths to achieve decarbonation and reduced energy consumption. We label this Domain Applications.
The Energy Transition solutions are enabled by a technology tool box. At a macro-level, each solution comprises a combination of electrical equipment (energy funnel), some form of modern electronics and automation for improved efficiency, and machine/system learning for smarter outcomes. Most comprehensive solutions will draw from all boxes, more focused solutions from a single box.
Take shipping. Around 90% of goods travel by sea, with 90%+ vessels propelled by diesel or gas engines. The decarbonation path will combine Clean Energy, Renewable Power, Power Storage to replace carbonated fuels, electric propulsion replacing mechanical shafts for greater power efficiency (electrification), a smarter use of on-board electric power through modern power electronics and automation (smart grids), and machine learning to set vessel controls for optimal power consumption based on internal (vessel shape and condition, load, machine specifications, targeted arrival date, …) and external (weather, current, depth, etc) inputs. Ultimately, the most sophisticated outcomes target autonomous vessels.
Take CO2 emissions. In order to reduce emissions, companies and consumers will need to track their own emissions as a starting point, to then engage in reducing their CO2 footprint. The tracking applies across the value-chain, from direct emissions (from using, making and delivering products and services), to the energy sources providing the power consumed, and the emissions up and down the value chain, including the lifetime emissions of products sold and emissions related to product recycling. A massive task. Tracking solutions are emerging that draw from the complex exercize of capturing and sharing data across stakeholders, and making a smart use of such data to change consumption patterns through algorythms, artificial intelligence, automation, power electronics.
At EssentiAll, we understand your playing field and how that translates into your value-proposition, business model, and growth strategy. We can learn from each other. Let’s talk !
